Telecom operators are constantly investing massive amounts of money into network transformation projects (4G, 5G, SDN, NFV, FTTx, etc.) to address their customers’ increasing demands. Network transformations bring new network capabilities, but at the same time, also require OSS and BSS transformations to support the delivery of new services to end customers.
OSS and BSS transformations are often neglected and are not being conducted simultaneously with the network transformation. Their absence brings telecom operators complications and unsatisfactory monetization of new network capabilities.
Such discrepancy lies in the fact that within telecom organizations, network departments often have a higher profile than the OSS and BSS departments. OSS and BSS departments are often completely separate from the network departments, and network departments tend to move more quickly than OSS and BSS departments. This is the source of the problem and telecoms should be looking at transforming the network in tandem with OSS and BSS systems.
A telecom can invest billions in the best network technology, but to get this technology to the customer so that it is usable, OSS and BSS systems must be in place.
Why should a telecom operator invest in relatively new OSS and BSS systems? Let’s first try to demystify what OSS and BSS systems actually do and why they are so important for telecom operators.
So, let’s start from the beginning.
What do operators need to do business?
The most important ingredient is the customers. To be more accurate, a geographical area with potential customers living and working in it. The second ingredient is the fixed and mobile network covering this area.
But the better question is, what do operators need to make a successful business?
The answer to this question is more complex, and raises a handful of additional questions, but we all can agree the following points are essential for running a telecom business successfully:
- Ability to quickly introduce new attractive services to ensure sources of revenue
- Ability to activate services quickly and accurately
- Ability to solve unexpected technical problems reasonably fast
- Ability to control costs and minimize unnecessary waste of money
- Ability to charge for the services consumed by the customers
- Ability to keep customers happy by providing a good customer experience
All these items are covered by the systems called Operations Support Systems and Business Support Systems – OSS and BSS.
Telecoms are constantly changing and evolving, keeping pace with new technologies, so the OSS and BSS systems also need to adapt to these changes in parallel.
What does OSS mean in telecom?
Let’s try to answer this question with a few simple examples.
Network planning is usually a starting point before building a new or transforming an existing network. The network needs to be carefully planned in order to be cost-effective and to give the best results. It may need to cover different geographic profiles, like mountains, valleys, islands, villages, and urban city areas to reach every customer. Twenty-five years ago, it took a team of experienced engineers in a room full of maps to plan the future network. Today it is all automated, thanks to OSS.

After the planning has been finished, approved, and the budgets have been allocated, the network needs to be built.
During the exploitation of the network, it is not uncommon that the surrounding area will be changed. For example, new skyscrapers can be constructed or a football stadium that attracts thousands of people can be built. Even though the network has been carefully planned and built, there is a constant need for network optimization – a process that never really ends and is made possible thanks to OSS.
Activation of services sold to end-customers, and getting people to start using all the things the telecom operator can offer – like calling, texting, surfing, watching TV and so on – on all sort of devices, fixed and mobile, in all kind of locations, is called service fulfillment. This involves the automatic configuration of different parts of the network and platforms, delivered by different vendors, working together, communicating, and acting as a unified system in the eyes of the end customer. All of this is again made possible thanks to OSS.
Service operation center is the heart of OSS in telecom
Imagine that suddenly, for some unexpected reason, a base station goes down, or construction workers damage the optical cable connecting your house. There is a department in every telecom called the Network Operations Center (NOC), where people working in it can detect the slightest disturbance in the network

The primary focus of Network Operation Centers was monitoring network equipment like routers and set-top-boxes, while today, people working in a NOC are focused on the monitoring of services running through the network. These days, many telecoms do not use the term NOC, but instead they are referred to as Service Operation Centers – SOC or Service Management Centers – SMC. Regardless of the terminology, the role of such a department is called service assurance and is made possible thanks to OSS.
How does BSS support commercial and customer-facing activities in telecom?
But operators also need to make money. It is a business, after all. They need to manage their revenue.
Some customers might have a postpaid subscription, while some are using prepaid cards. Some might have a certain amount of free minutes, while others might have some free data. Regardless of the options the customer has, there must be a mechanism for accurate billing and charging. These systems ensure that the customer pays the correct rate for services used at different locations at different periods of time.
Also, there must be automatic up-sale mechanisms to increase revenue of a telecom operator by selling more services to the customer. In cases when the customer uses all the Internet traffic included in his data plan, the data rate can be automatically reduced, but at the same time the customer gets a text message to purchase more data at full speed. All these processes are an integral part of the BSS system.
When customers need to contact their operator, report a problem with a service, change a billing address, or just ask a question about services, they need to turn to the customer support department. The application to handle these processes is called Customer Relationship Management, or CRM, which is also part of the BSS system.
OSS and BSS working together to run a network and business effectively
These are just a few of the processes covered by OSS and BSS systems, but even from these few examples, it is visible that OSS and BSS systems are the life-blood of every telecom making the technology and customer experience come together.
The size and complexity of today’s multi-vendor telecommunication networks is enormous. Huge volumes of data need to be processed and analyzed in a near real time with a single goal to ensure stable revenue stream for the telecom and to keep the customer satisfied. There are currently more than 25 billion connected devices worldwide, with an estimated 50 billion by 2030.
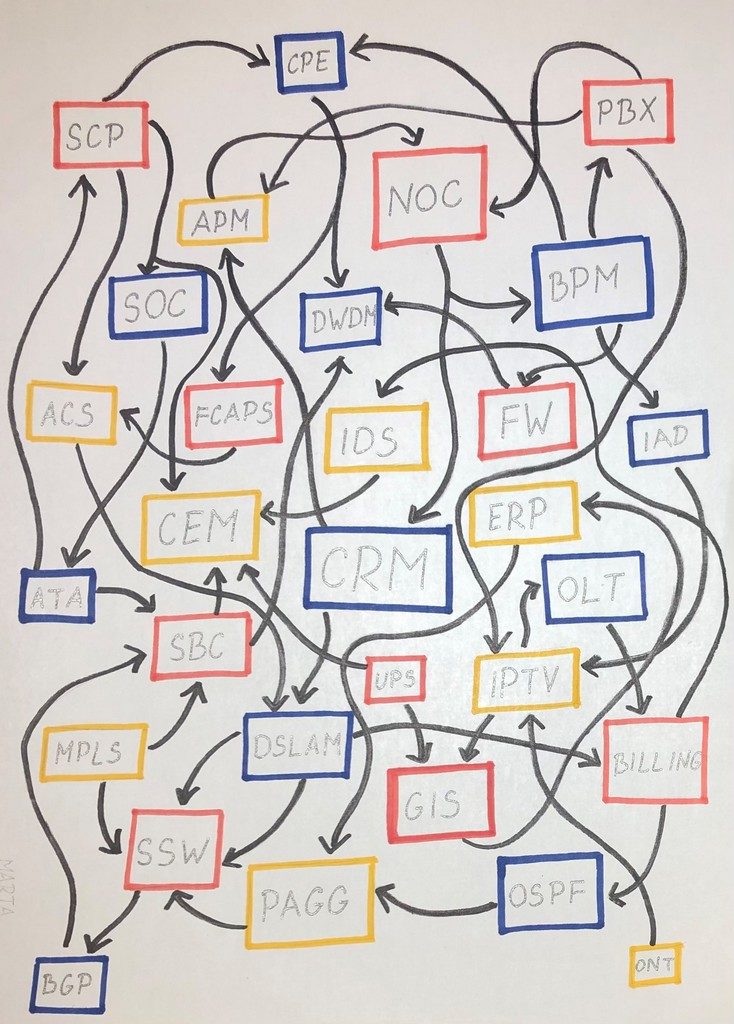
Running a telecom business today is fundamentally different than it was twenty or thirty years ago. The level of complexity of telecom networks, platforms and services has moved beyond the limits of human comprehension. Telecoms do not have any other option but to strongly rely on modern OSS and BSS systems implementing advanced analytics and artificial intelligence capabilities, to make optimal decisions, keep their business competitive and customers satisfied.
OSS and BSS provide the best ways to run a network and the best ways to run a business.










